Selection and Trends for Electric Forklifts in 2026
What is an electric forklift?
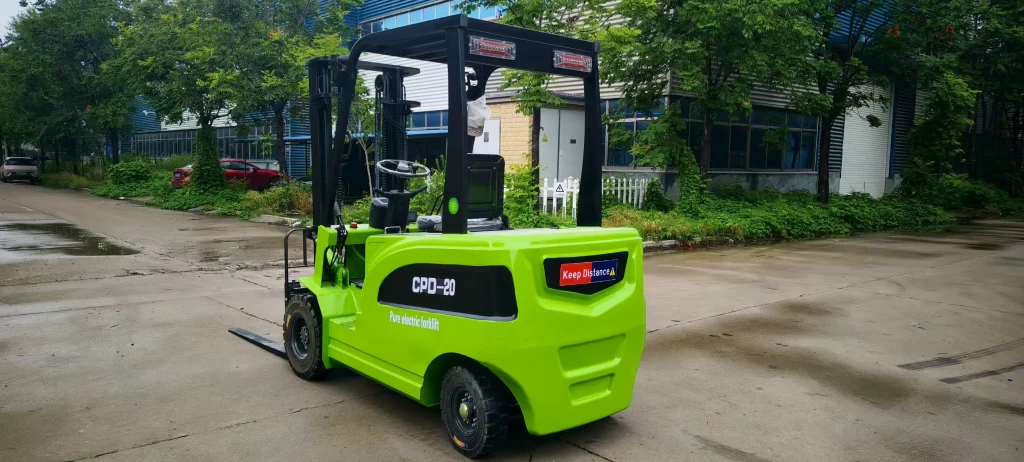
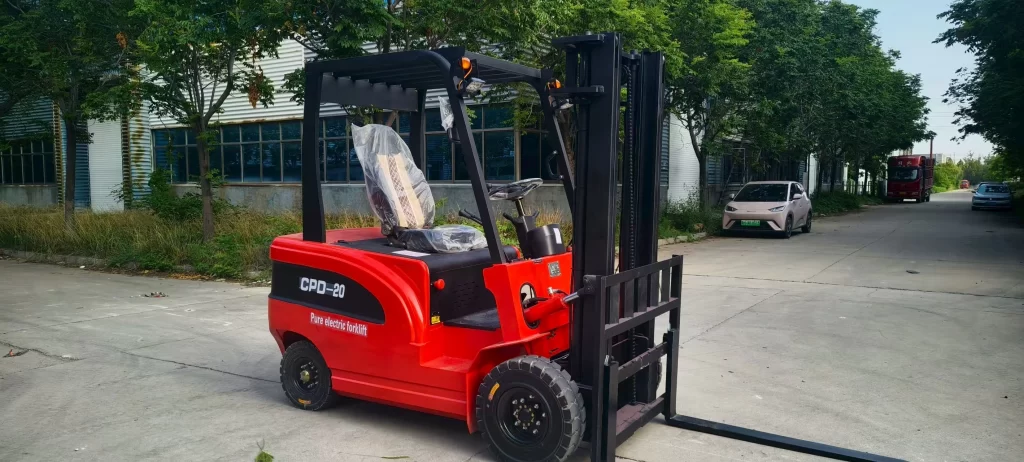
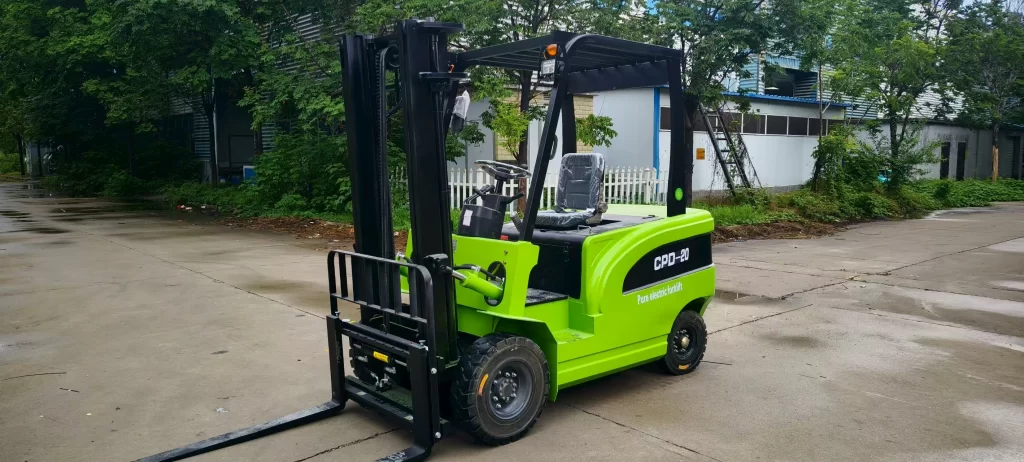
An electric forklift is a material handling device powered by a battery, converting chemical energy into electrical energy for operation. Primary classifications include counterbalanced electric forklifts, stand-up stackers, four-way electric forklifts, electric pallet trucks, and walkie stackers. They utilize dual controllers to enhance lifting capacity and maneuverability, featuring pollution-free operation, ease of use, energy efficiency, and high performance. For daily battery maintenance, avoid laying batteries horizontally and regularly replenish distilled water. Our electric forklifts employ maintenance-free lead-acid batteries for power, capable of supporting 3,000 charge-discharge cycles.

Electric Forklift Classification
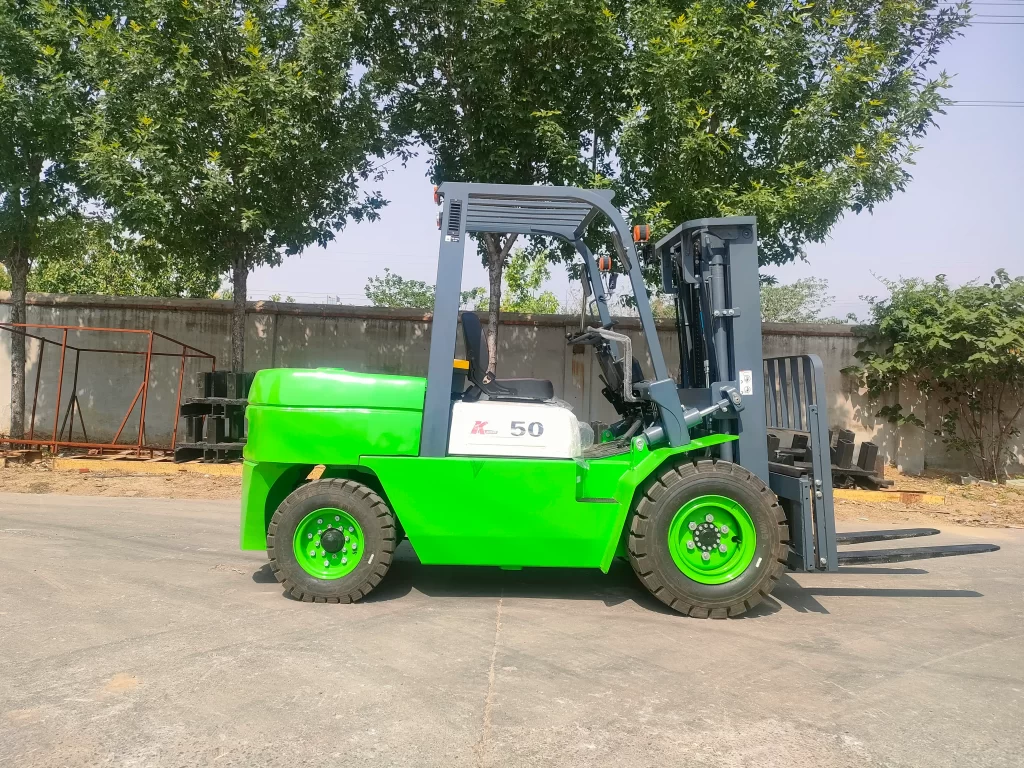
These electric material handling vehicles can be categorized as: four-way electric forklifts, electric pallet stackers, walkie electric stackers, electric tow tractors, three-point electric forklifts, four-point counterbalanced forklifts, reach trucks, three-point mini forklifts, ammunition counterbalanced forklifts, cold storage electric forklifts, electric explosion-proof forklifts, pedestrian counterbalanced forklifts, electric drum stackers, three-point leg-insert stackers, workstation cranes, four-point leg-insert stackers, four-point wide-leg stackers, pallet rack order pickers, four-point double-deck stackers, electric tow tractors, order pickers, and other electric material handling equipment.
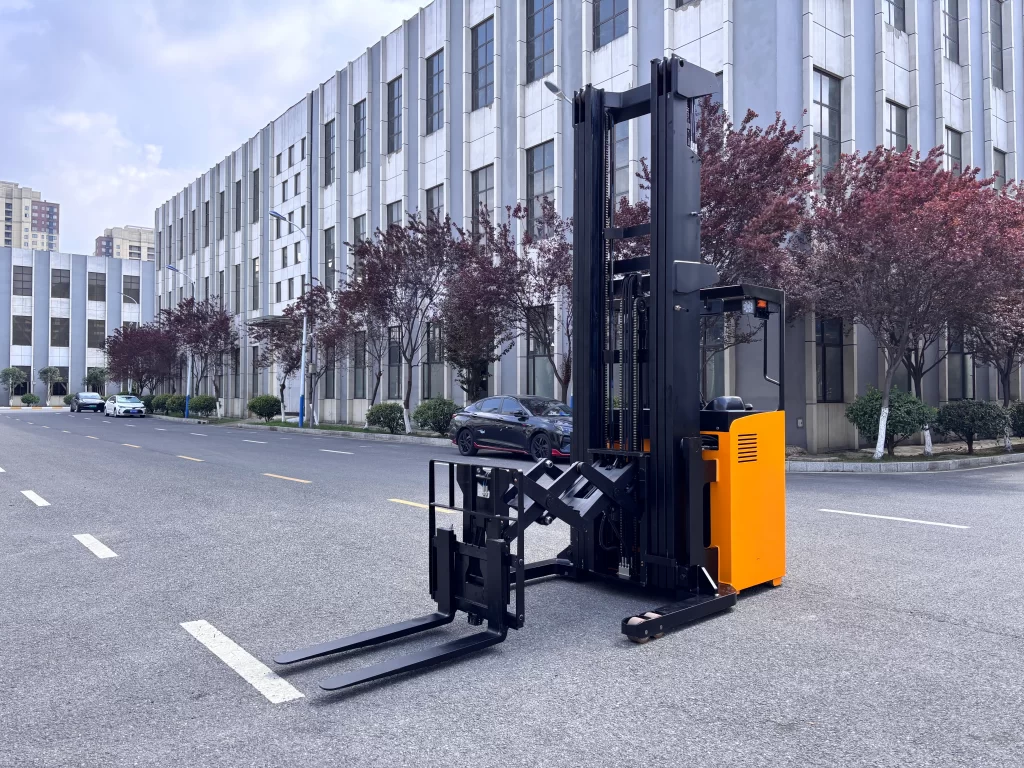




Principle of Electric Forklifts
Battery-powered forklifts utilize rechargeable batteries as their primary power source to drive both the traction motor and hydraulic system motor, enabling both travel and material handling operations. Electric forklifts are loading/unloading and material handling vehicles powered by direct current (batteries). The most significant advancement in new materials and processes is the application of transistor controllers (SCR and MOSFETs). Their introduction has greatly enhanced the performance of electric forklifts, significantly improving overall durability, reliability, and adaptability, making them fully competitive with internal combustion engine forklifts.
Advantages of Electric Forklifts
Beyond their simple operation and flexibility, electric forklifts impose considerably less physical strain on operators compared to internal combustion models. Their electric steering systems, acceleration controls, hydraulic systems, and braking mechanisms are all electrically signaled, substantially reducing operator fatigue. This significantly boosts work efficiency and precision. Moreover, compared to internal combustion forklifts, electric vehicles’ low noise levels and zero exhaust emissions have gained widespread user recognition. Additionally, technical advancements drive the adoption of electric forklifts. Rapid developments in electronic control technology have made electric forklift operation increasingly comfortable, expanded their applicability, and provided more diverse logistics solutions. Considering these factors, market demand for electric forklifts will undoubtedly grow at an accelerating pace, with their market share steadily increasing.
Electric forklifts utilize electric drive systems, offering advantages such as pollution-free operation, ease of handling, energy efficiency, and high performance compared to internal combustion models. Driven by economic growth and heightened environmental and energy conservation demands, electric forklifts are experiencing rapid development with steadily rising market sales. Particularly in ports, warehousing, and industries like tobacco, food processing, and light textiles, electric forklifts are progressively replacing internal combustion counterparts.
Daily Operation
Operating Procedures
- Maintain an appropriate starting speed; avoid abrupt acceleration.
- Monitor the voltage on the voltmeter. If it falls below the limit voltage, immediately stop the forklift.
- While moving, do not switch the directional control to change course, as this may burn out electrical components or damage gears.
- Avoid simultaneous travel and lifting operations.
- Monitor the drive and steering systems for abnormal sounds. Address any unusual noises promptly; never operate with malfunctions.
- Decelerate in advance when changing direction.
- Reduce load weight and lower travel speed when operating on poor road conditions.
Precautions
- 1. Verify cargo weight before lifting; never exceed the forklift’s rated capacity.
- 2. When lifting packaged goods, ensure the packaging is securely fastened.
- 3. Adjust the fork spacing according to the cargo dimensions to distribute the load evenly between the forks and avoid uneven loading.
- 4. When inserting the forks into the load, tilt the mast forward. After loading the cargo onto the forks, tilt the mast backward to position the load close to the fork walls. Lower the load as much as possible before moving.
- 5. Lifting and lowering operations should generally be performed in a vertical position.
- 6. When performing manual loading/unloading, engage the hand brake to stabilize the forks.
- 7. Do not operate travel and lift functions simultaneously.
- 8. When transporting cargo on steep inclines, ensure the load remains securely positioned on the forks.
Key Considerations for Selection
Electric forklifts, as the name suggests, are powered by electricity, primarily supplied by batteries. When selecting one, we should consider not only its external appearance and performance but also its internal components.
Below, we’ll guide you on how to choose a cost-effective electric forklift.
- Compare prices. Manufacturers typically offer significantly lower prices than sales agents.
- Review operating time specifications carefully. Some unscrupulous sellers may label extended usage durations that do not reflect continuous operation. You must assess the actual working hours of the electric forklift and select accordingly to maximize efficiency.
- Gain a clear understanding of fundamental factors like price, specifications, performance, and brand reputation. This knowledge allows you to leverage past experience when evaluating options during purchase.
- To find the best value, multiple quotes and comparisons are essential. If you prefer simplicity, opt for a high-quality model directly.
- Safety is the paramount consideration when evaluating forklifts.
Key points include:
- Load handling: To prevent cargo damage, prioritize forklifts with high operational stability to avoid costly consequences.
- Operator safety: Human operation inherently carries risks. Personal safety must always be the top priority, so electric forklift quality is absolutely non-negotiable.
- Essentially, by keeping these five points in mind, a quality electric forklift won’t escape your discerning eye.
- Daily Maintenance
- Regularly top up the battery with distilled water (pure water).
- When the electric forklift is not in use for extended periods, fully charge the battery and store it. Recharge the battery approximately every 1-2 months.
- For multi-shift operations, motor-driven warehouse forklifts require spare batteries (continuous operation drains battery power quickly and causes significant wear).
During battery charging, completely disconnect the charging circuit from the chopper. This prevents interference with the charger and protects the chopper from damage caused by overvoltage generated by the charger.
- Do not store batteries horizontally.
- Use an intelligent multi-stage charger to prevent overcharging and water loss.
- Opt for high-efficiency electric hub systems to reduce operating current.
- Charge frequently or maintain a reasonable charging frequency, ideally following a scheduled regimen (e.g., daily or every other day).
- Avoid storing batteries in a discharged state, as this is most detrimental to battery health.
Precautions
During charging and discharging, water in the electrolyte gradually diminishes due to electrolysis and evaporation, causing the electrolyte level to drop. Failure to replenish promptly may shorten battery life. Distilled water should be added immediately. Never substitute purified drinking water, as its trace elements can adversely affect the battery.
When adding electrolyte or water:
– Maintain a level 10-15mm above the plates.
– For batteries with dual red lines, electrolyte must not exceed the upper red line. Overfilling electrolyte may cause it to overflow through the battery cap’s small vent hole. If it flows between the positive and negative terminals, it can create a circuit and cause self-discharge. In such cases, wipe away the electrolyte or rinse and clean the area with boiling water.
If foreign objects accidentally fall into the electrolyte during refilling, never use metal tools to retrieve them. Instead, use a wooden stick to remove debris. Using iron or copper wire could cause metal molecules to enter the battery through sulfuric acid corrosion, leading to self-discharge and battery damage.
If a vehicle remains idle for over 20 days, disconnect the battery’s negative terminal cable to prevent leakage accidents.
Trends in Electric Forklifts
Google Trends data shows electric forklifts consistently in an upward phase. Daily searches indicate significant interest in purchasing electric forklifts locally or online.
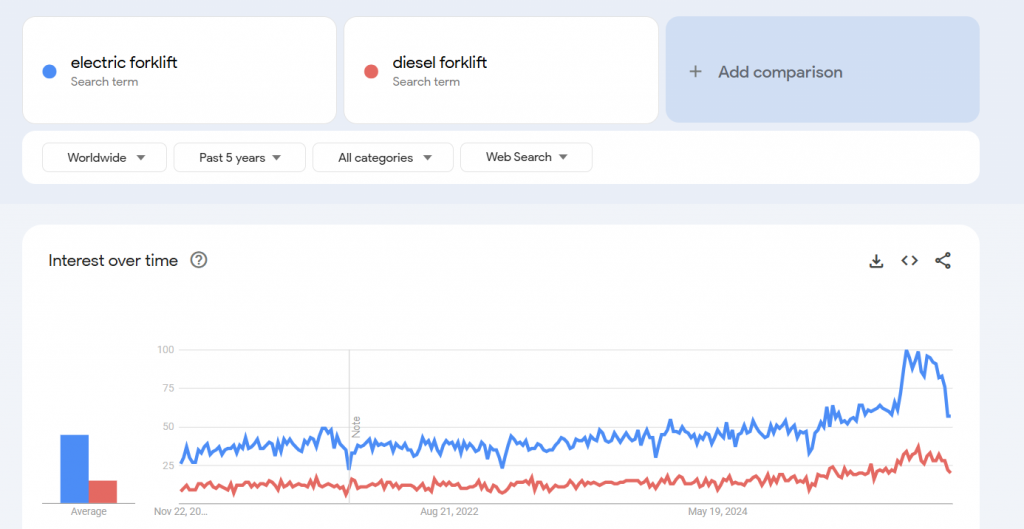
Low cost and environmental friendliness are key considerations for users. Taking a 4-ton counterbalanced forklift as an example, a lithium-ion model reduces annual carbon emissions by 6,900 kilograms compared to a diesel counterpart, significantly contributing to emission reduction. Featuring electronic steering systems and electrical signal controls, this equipment is widely adopted in ports, warehouses, and food industries. Moreover, electricity costs less than diesel or gasoline, making electric forklifts more economical than internal combustion models in both initial and long-term expenses.
Smart electric forklifts and warehouses represent a major future trend, with unmanned warehouses and automated operations marking significant progress in the logistics industry.




